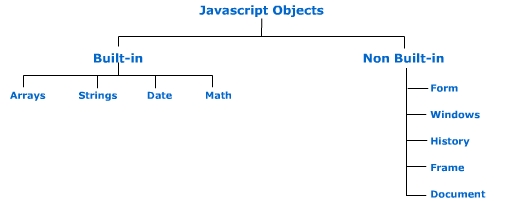

Lets see what are built-in functions and commands related to them.
Array Object: Arrays are set of characters or numbers or generally consists of some value.
The commands related to the Array Object are :
|
tostring() |
join(seperator) | reverse() | sort() |
e.g.
<html>
<head>
<script>
myarray = [3, 8, 5, 1, 9, 0, 6, 2, 7, 4]
document.write ("myarray is : "+myarray+" ");
document.write ("myarray.toString() is : "+myarray.toString()+"
");
document.write ("myarray.join(':') is : "+myarray.join(':')+"
");
document.write ("myarray.reverse() is : "+myarray.reverse()+"
");
document.write ("myarray.sort() is : "+myarray.sort()+"
");
</script>
</head>
</html>
String Object : Strings are arrays of characters.
e.g.
<html>
<head>
<script>
var s = ("This is a test a of JAVASCRIPT string methods.")
document.write ("String s is : "+s+" <br> ");
document.write ("s.charAt(1) : "+s.charAt(1)+" <br>
");
document.write ("s.charCodeAt(8) : "+s.charCodeAt(8)+"
<br> ");
document.write ("s.indexOf('is') : "+s.indexOf('is')+"
<br> ");
document.write ("s.lastIndexOf('is') : "+s.lastIndexOf('is')+"
<br> ");
document.write ("s.substring(20,30) : "+s.substring(20,30)+"
<br> ");
document.write ("s.toLowserCase() : "+s.toLowerCase()+"
<br> ");
document.write ("s.toUpperCase() : "+s.toUpperCase()+"
<br> ");
document.write ("s.split(' ') : "+s.split(' ')+" <br>
");
split = s.split(" ")
for ( i=0; i < split.length; ++i )
document.write (" split ["+i+"] = "+split[i]+" <br>");
</script>
</head>
</html>
DATE Object
: The DATE Object provides a common set
methods for working with dates & times.
These methods are summarized in table.
The methods with UTC in their name refer to Universal
Coordinated Time, which is
time set by world time standard.
|
getDate() |
getDay() |
getHours() |
getMinutes() |
getYear() |
e.g.
<html>
<head>
<script>
day = new Date();
a = day.getDate();
b = day.getHours();
c = day.getMinutes();
d = day.getSeconds();
e = day.getYear();
f = day.getDay();
g = day.getMilliseconds();
v = day.getUTCDay();
u = day.getTime();
x = day.getUTCDate();
y = day.getUTCHours();
z = day.getUTCMinutes();
w = day.getUTCSeconds();
m = day.getUTCMilliseconds();
document.write ("Year : " + e + " <p>");
document.write ("Day : " + f+" <br>")
document.write ("Date : " + a + " <br>") ;
document.write ("Hour : " + b + " <br>");
document.write ("Minutes : " + c + " <br>");
document.write ("Seconds : " + d + " <br>");
document.write ( "Milliseconds : " + g + " <p>");
document.write ("UTCDay : " + v + " <br>");
document.write ("UTCDate : " + x + " <br>");
document.write ("UTCHour : " + y + " <br>");
document.write ("UTCMinutes : " + z + " <br>");
document.write ("UTCSeconds : " + w + " <br>");
</script>
</head>
</html>
The Math
Object: The Math
Object enables you to carry out the mathematical calculations in the web page.
The various commands are listed below.
| abs(x) - absolute value of x | acos(x),cos(x) - arc cos & cos of x | asin(x),sin(x) - arc sin & sin of x |
| atan(x),tan(x) - tan & arc tan of x | ceil(x) - x rounded up to nearest integer | exp(x) - e raised to x power |
| floor(x) - x rounded up to nearest integer | sqrt(x) - square root of x | pow(x,y) - x raised to y power |
| max(x,y) - maximum or x and y | min(x,y) - minimum or x and y | log(x) - logarithm of x |
Non builtin Objects are part of web page model on which javascript implements its commands.
There are as such many non builtin objects, for e.g Window, Location, History, Frame etc..
We will see all objects one by one.
Window Object:e.g
<html>
<head>
<script>
function open()
{
window.open("hi.htm");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<Input type="button" value="Open Window"
Onclick="window.close()">
</form>
</body>
</html>
History
Object:
<html>
<body>
<a href="Javascript:history.back()">History
Object - Click here</a>
</body>
</html>
Similarly you can use
Javascript:history.go(num) ,
Javascript:history.previous (same as history.back() ),
Javascript:history.next